ProSynn
An Educational App on Protein Synthesis

Motivation: From Classroom to Code
During my undergraduate biotechnology course in 2016, I had the opportunity to dive deep into one of the most fascinating processes in biology: protein synthesis. This process, where cells produce the proteins necessary for life, intrigued me so much that I decided to take my learning beyond textbooks and lectures. I wanted to create something interactive, something that could make learning this complex process engaging and fun. That’s how I ended up developing an educational app on protein synthesis using the Unity engine (v5.4.2f2) for multiple platforms including android, windows and linux.
Understanding Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is a crucial process that occurs within the cells of all living organisms. It’s the method by which cells create proteins, essential molecules that perform a wide range of functions, from building cellular structures to facilitating chemical reactions. The process of protein synthesis is composed of two main stages: transcription and translation.
Transcription takes place in the nucleus of the cell. During this stage, the DNA sequence of a gene is used as a template to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA consists of four nucleotide bases: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G). When DNA is transcribed into RNA, a small change occurs: the base Uracil (U) replaces Thymine (T). So, RNA is made up of Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G).
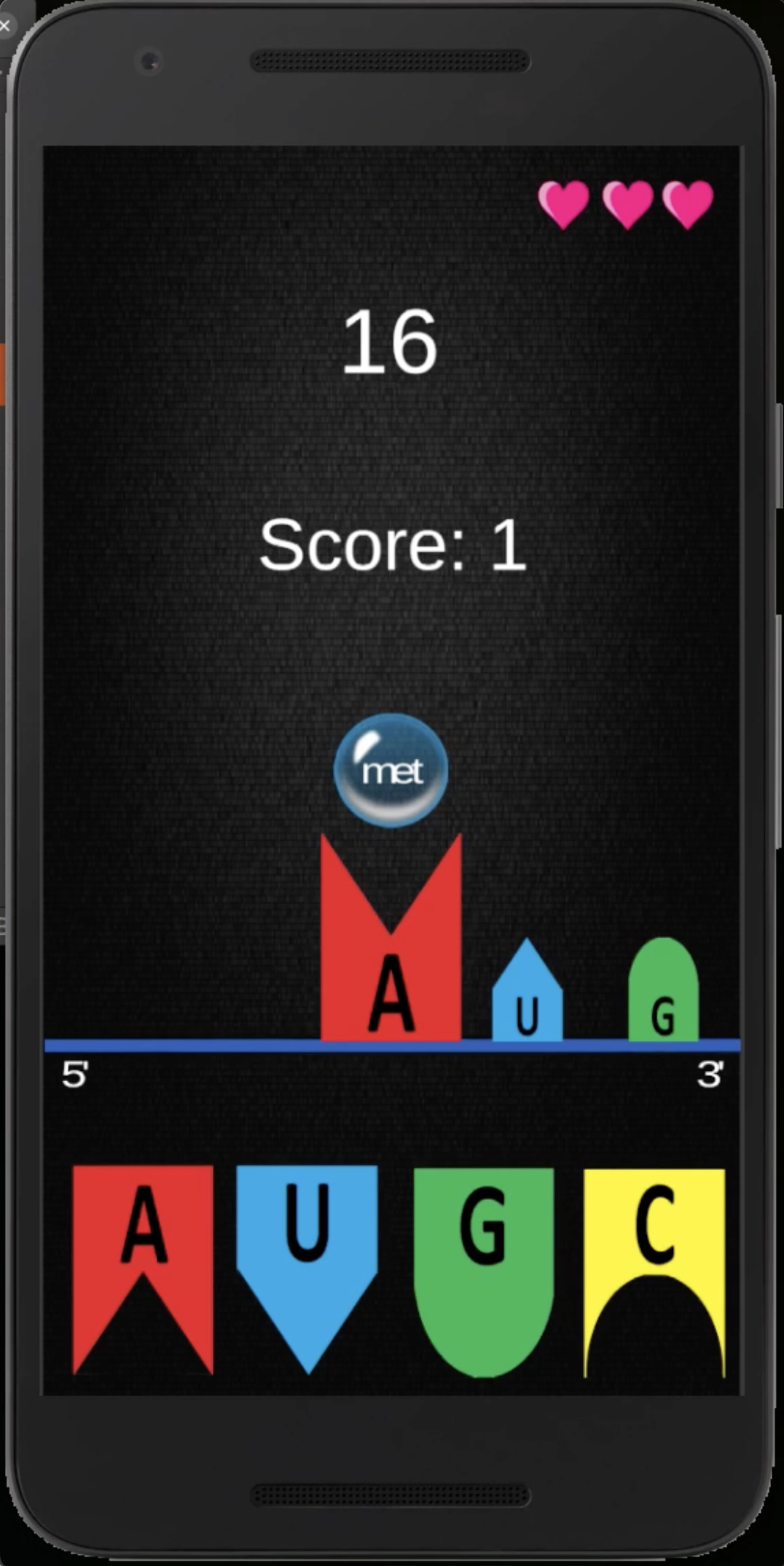
Once the mRNA is produced, it leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. During translation, the mRNA is read by the ribosome, which synthesizes a protein by stringing together amino acids in a specific order. The mRNA is read in groups of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or a signal to start or stop protein synthesis. For example: AUG is the start codon, which also codes for the amino acid methionine. GCU codes for the amino acid alanine.
The sequence of these codons on the mRNA determines the sequence of amino acids in the protein. This process continues until a stop codon (such as UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered, signaling the end of protein synthesis. The pairing of nucleotides is also crucial in this process. In RNA: Adenine (A) pairs with Uracil (U). Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G). These pairings ensure that the genetic code is accurately translated into the protein’s amino acid sequence.
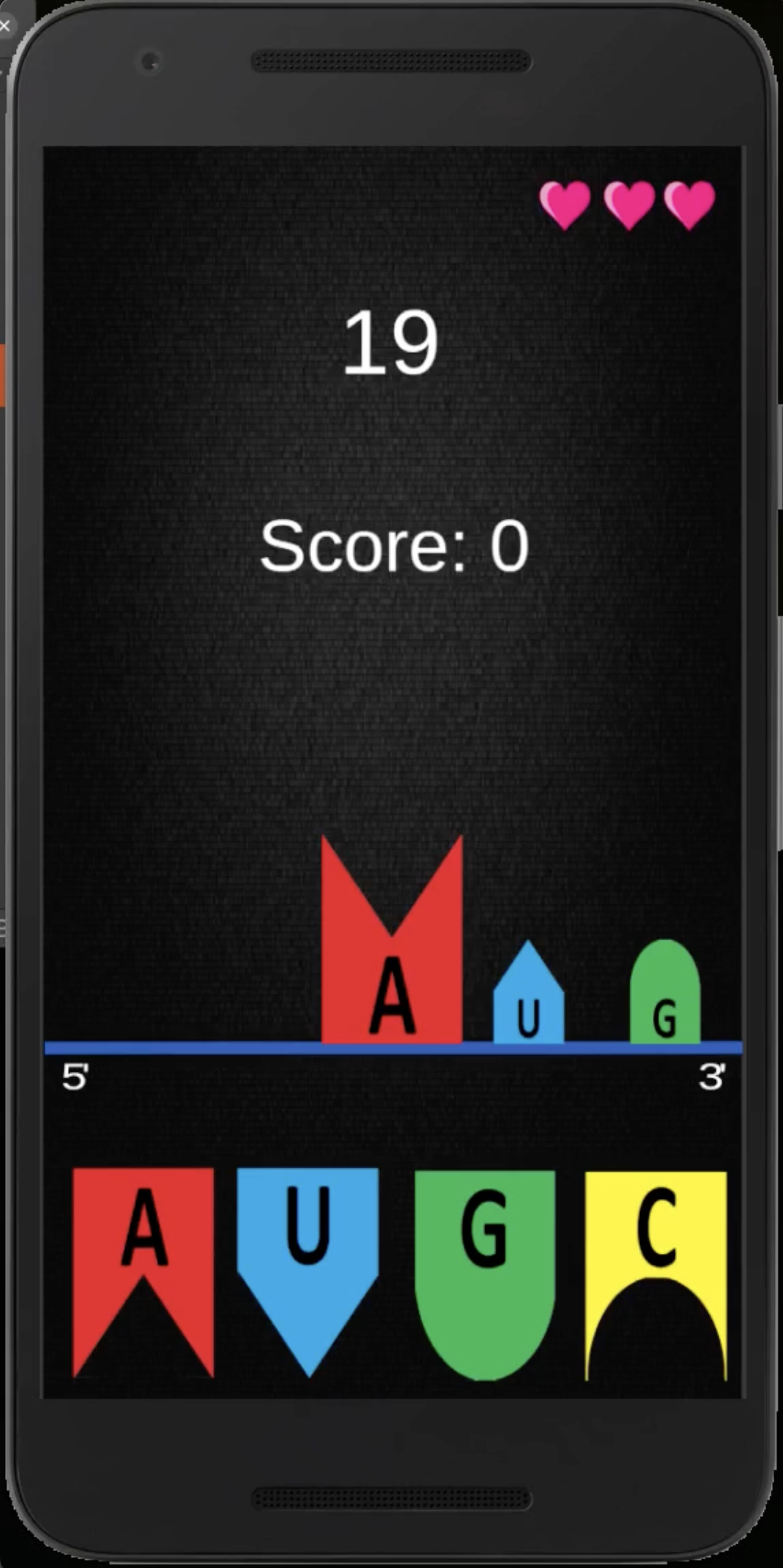
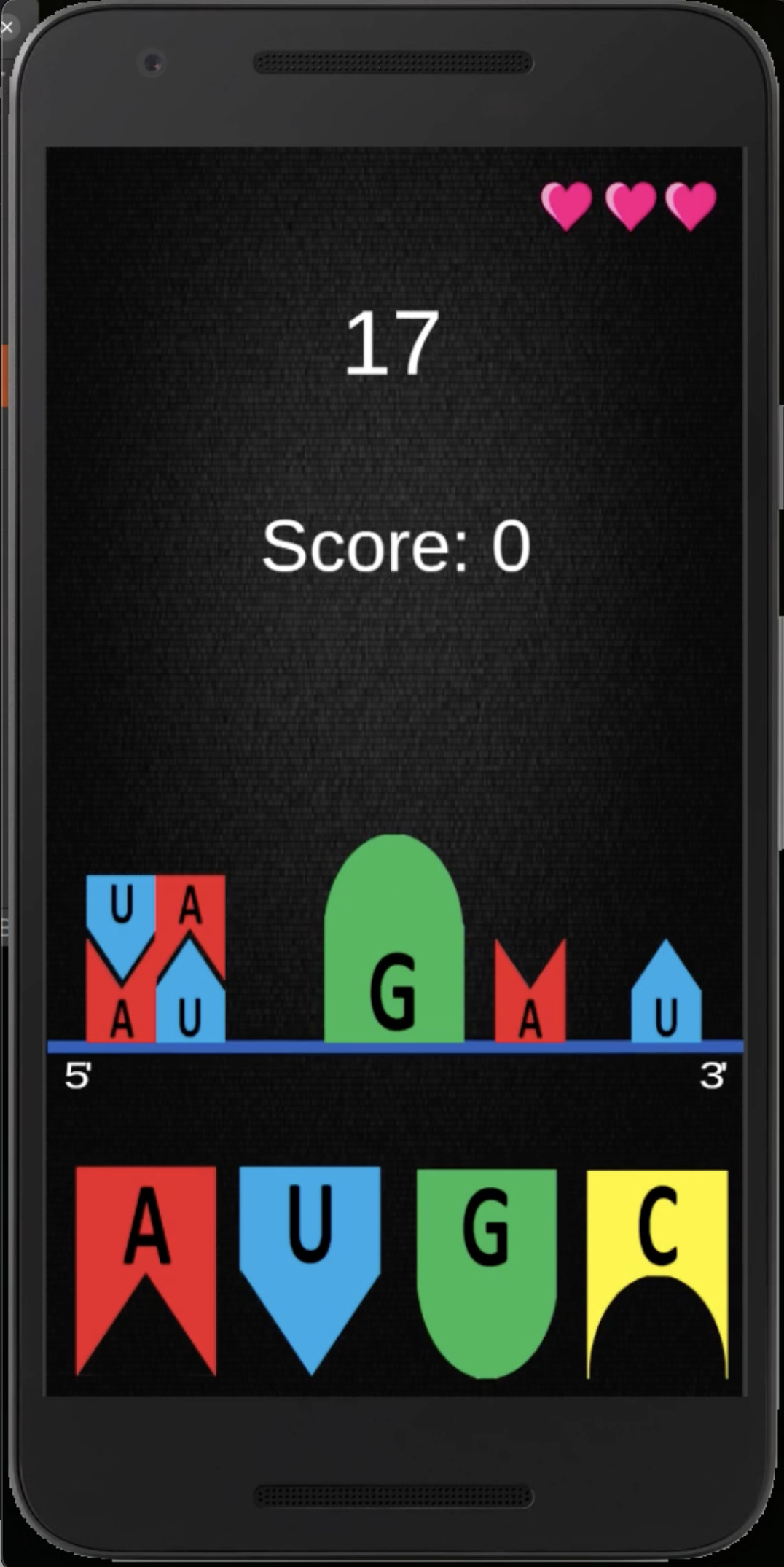
The Game: Synthesizing Proteins
In the educational app I developed, the objective is to synthesize as many proteins as possible within a given time (10, 20 or 30 secs). The game challenges players to correctly pair mRNA codons to form the correct amino acids, mimicking the translation process. To add a layer of difficulty, players are allowed only two mistakes before the game ends. This approach not only makes learning about protein synthesis interactive but also reinforces the importance of accuracy in this biological process.
Developing this app was a rewarding experience, as it allowed me to blend my passion for science with my interest in game development. I hope that through this app, others can find the same fascination with protein synthesis that inspired me during my studies.